Collection과 Generics에 대한 사전지식없이
Arraylist를 사용하기엔 문제가 있을것 같아
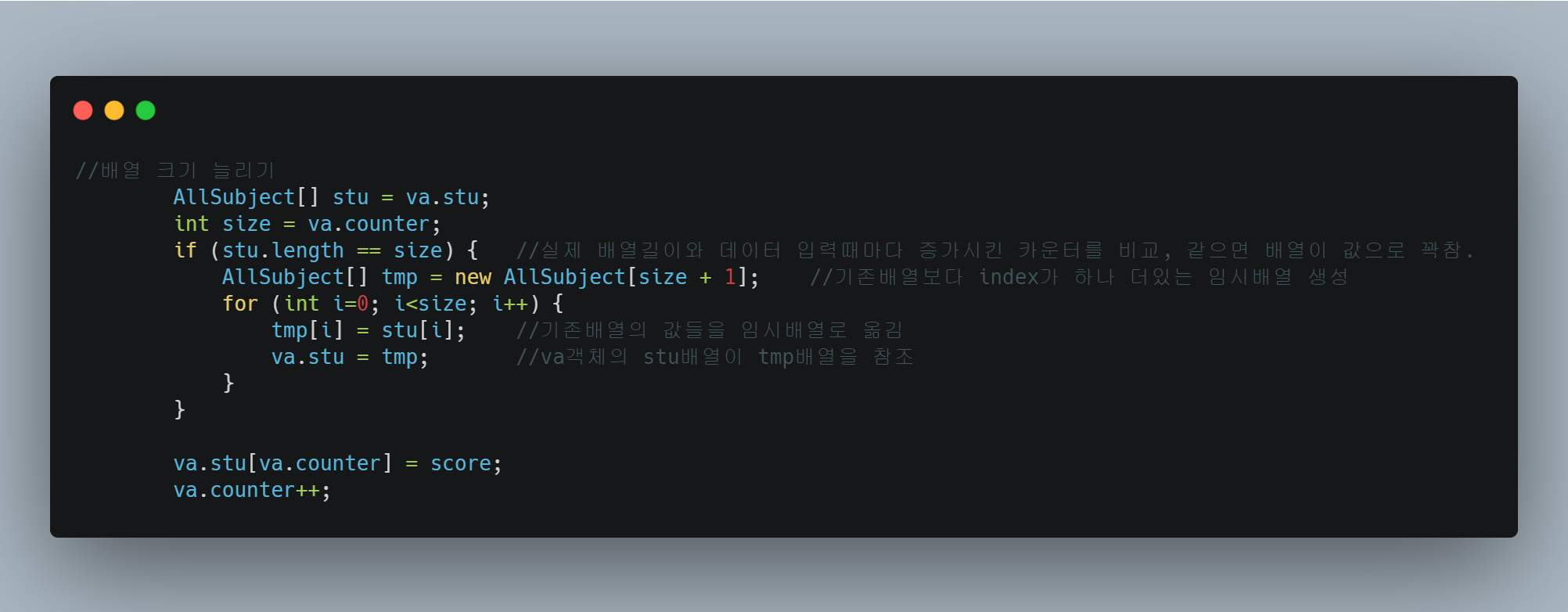
기존 고정길이배열에서 배열길이를 늘리면 값을 받는 코드를 만들었다.
|
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AllSubject {
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
}
public class VariableArray {
AllSubject[] stu;
int counter;
}
public class MakeArraylist {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String... args) {
VariableArray va = new VariableArray();
va.stu = new AllSubject[2];
va.counter = 0;
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
int m = menu();
switch (m) {
case 1:
input(va);
break;
case 2:
output(va);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("프로그램 종료.");
loop = false;
break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 값을 입력하셨습니다. 메뉴는 1~3까지입니다.");
}
}
sc.close();
}
private static void output(VariableArray va) {
int size = va.counter;
AllSubject[] stu = va.stu;
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
AllSubject score = stu[i];
int kor = score.kor;
int eng = score.eng;
int math = score.math;
int total = score.kor + score.eng + score.math;
float avg = total / 3.0f;
System.out.println("국어: " + kor);
System.out.println("영어: " + eng);
System.out.println("수학: " + math);
System.out.println("총점: " + total);
System.out.println("평균: " + avg);
System.out.println("────────────────────────");
}
}
private static void input(VariableArray va) {
System.out.println(" -성적 입력-");
int kor, eng, math;
do {
System.out.printf("국어: ");
kor = sc.nextInt();
if (kor < 0 || 100 < kor) {
System.out.println("성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
} while (kor < 0 || 100 < kor);
do {
System.out.printf("영어: ");
eng = sc.nextInt();
if (eng < 0 || 100 < eng) {
System.out.println("성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
} while (eng < 0 || 100 < eng);
do {
System.out.printf("수학: ");
math = sc.nextInt();
if (math < 0 || 100 < math) {
System.out.println("성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
} while (math < 0 || 100 < math);
AllSubject score = new AllSubject();
score.kor = kor;
score.eng = eng;
score.math = math;
AllSubject[] stu = va.stu;
int size = va.counter;
if (stu.length == size) {
AllSubject[] tmp = new AllSubject[size + 1];
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
tmp[i] = stu[i];
va.stu = tmp;
}
}
va.stu[va.counter] = score;
va.counter++;
System.out.println("────────────────────────");
}
private static int menu() {
System.out.println(" -메인 메뉴-");
System.out.println("\t1. 성적입력 ");
System.out.println("\t2. 성적출력 ");
System.out.println("\t3. 종료 ");
System.out.print("\t선택> ");
int menu = sc.nextInt();
return menu;
}
}
|
cs |
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 왜 객체변수명을 클래스명과 통일시키는가? (0) | 2021.11.09 |
|---|---|
| OOP - 캡슐화 (0) | 2021.11.08 |
| 배열 객체를 생성해서 다수의 성적 입출력 (0) | 2021.11.01 |
| 객체 생성, 메소드의 파라미터로 객체를 쓰는법 (0) | 2021.11.01 |
| 파라미터 - 메소드에서 전역변수 사용을 지양하기 (0) | 2021.10.26 |



